n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
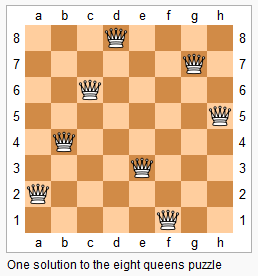
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q’ 和 ‘.’ 分别代表了皇后和空位。
解法
方法一:
修改了 N 皇后问题 I 中的解法,最终运行效率击败 55%
class Solution {
public:
int res;
vector<bool> col,dig1,dig2;
int totalNQueens(int n) {
col=vector<bool>(n,false);
dig1=vector<bool>(2*n-1,false);
dig2=vector<bool>(2*n-1,false);
vector<int> row;
res=0;
putQueen(row,n,0);
return res;
}
void putQueen(vector<int> row,int n,int index){
if(n==index){
res++;
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(!col[i] && !dig1[index+i] && !dig2[index-i+n-1]){
row.push_back(i);
col[i]=true;
dig1[i+index]=true;
dig2[index-i+n-1]=true;
putQueen(row,n,index+1);
col[i]=false;
dig1[i+index]=false;
dig2[index-i+n-1]=false;
row.pop_back();
}
}
return;
}
};方法二:(takaken的解法)
bitmap 解法,耗时 0ms,运用了位运算的一些方法,使得解题的效率大大提高
class Solution {
public:
int backtrack(int row, int hills, int next_row, int dales, int count, int n) {
/**
row: 当前放置皇后的行号
hills: 主对角线占据情况 [1 = 被占据,0 = 未被占据]
next_row: 下一行被占据的情况 [1 = 被占据,0 = 未被占据]
dales: 次对角线占据情况 [1 = 被占据,0 = 未被占据]
count: 所有可行解的个数
*/
// 棋盘所有的列都可放置,
// 即,按位表示为 n 个 '1'
// bin(cols) = 0b1111 (n = 4), bin(cols) = 0b111 (n = 3)
// [1 = 可放置]
int columns = (1 << n) - 1;
if (row == n) // 如果已经放置了 n 个皇后
count++; // 累加可行解
else {
// 当前行可用的列
// ! 表示 0 和 1 的含义对于变量 hills, next_row and dales的含义是相反的
// [1 = 未被占据,0 = 被占据]
int free_columns = columns & ~(hills | next_row | dales);
// 找到可以放置下一个皇后的列
while (free_columns != 0) {
// free_columns 的第一个为 '1' 的位
// 在该列我们放置当前皇后
int curr_column = - free_columns & free_columns;
// 放置皇后
// 并且排除对应的列
free_columns ^= curr_column;
count = backtrack(row + 1,
(hills | curr_column) << 1,
next_row | curr_column,
(dales | curr_column) >> 1,
count, n);
}
}
return count;
}
int totalNQueens(int n) {
return backtrack(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, n);
}
};